Currently, the prevailing industry standard for the Chinese solid surface industry is "JC/T 908-2013 Artificial Stone" under the Building Materials Industry of the People's Republic of China. In this article, we present excerpts related to the standards for artificial stone solid surface materials.
1.Terminology and Definitions
·Artificial Stone-Solid Surface Materials:
Artificial stone, also known as mineral-filled high polymer composite material, is primarily composed of methyl methacrylate (MMA, commonly known as acrylic) or unsaturated polyester resin (UPR) as the matrix. It mainly consists of aluminum hydroxide as filler, along with pigments and other additives. It is fabricated through casting, vacuum molding, or compression molding processes. This material is commonly referred to as solid surface.
Note: This composite material is non-porous and homogeneous throughout its thickness. It can be manufactured into seamless continuous surfaces, and its appearance can be restored to its original state through maintenance and refurbishment.
2.Product Classification, Specifications, and Grades
·Solid Surface Classification:
Artificial stone primarily composed of aluminum hydroxide as the main filler is categorized into two types based on the matrix resin:
1)Acrylic Type: Solid surface materials with polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) as the matrix resin (acrylic type, coded as PMMA).
2)Unsaturated Polyester (including vinyl ester resins, etc.) Type: Solid surface materials with unsaturated polyester resin (UPR) as the matrix resin (unsaturated type, coded as UPR).
·Specifications:
Sheets are categorized into three standard size forms based on their dimensions (length X width) X thickness, measured in millimeters:
I Type: (2440X760) X 12.0;
II Type: (2440X750) X 6.0;
HI Type: (3050X760) X 12.0.
Note: Other dimensions and thickness sizes may be agreed upon by both the supplier and the buyer, and these custom sizes are officially labeled as IV Type.
·Grades:
Products are classified into two grades based on Barcol hardness and falling ball impact: Premium Grade A and Qualified Grade B.
3 Materials
·Fillers or Pigments:
The fillers or pigments used in artificial stone must be appropriate materials that meet the performance requirements of this standard.
·Solid Surface Resins:
The polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and/or unsaturated polyester resin (including vinyl ester resins, etc.) used in artificial stone must be suitable materials that meet the performance requirements of this standard.
Specific requirements for solid surface materials, quartz stone, and granite stone are provided in Table.
Table 1: Requirements for Artificial Stone.
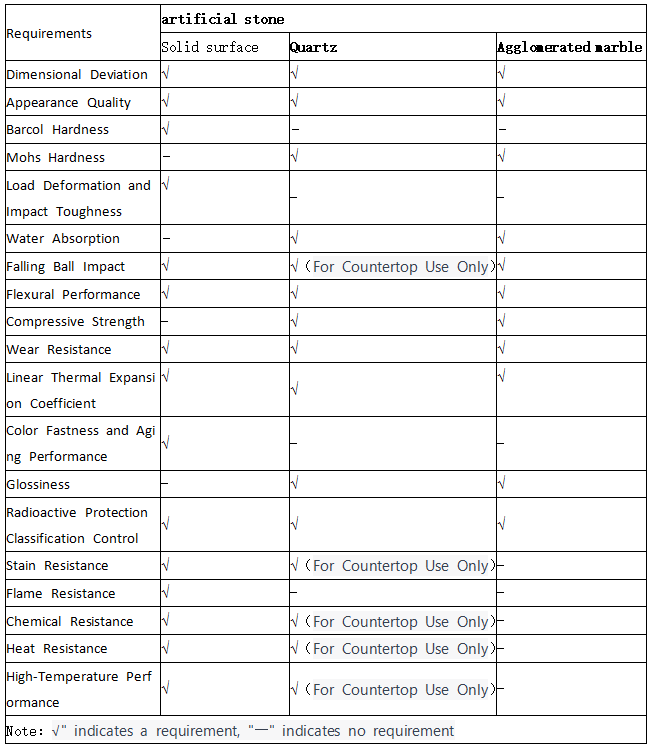
4.Dimensional Deviation
·Allowable values for length and width deviations are within 0% to 0.3% of the specified dimensions.
·Allowable values for thickness deviations are as follows: for thickness greater than 6 mm, not exceeding ±0.3 mm; for thickness not exceeding 6 mm, not exceeding ±0.2 mm.
·For other products, the allowable thickness deviation should not exceed ±3% of the specified thickness.
·Diagonal deviation: The maximum difference in diagonal measurements on the same sheet should not exceed 5 mm.
·Flatness: For I and Ⅲ types, the deviation should not exceed 0.5 mm; for II type, it should not exceed 0.3 mm.
·For other thickness products, the flatness tolerance should not exceed 5% of the specified thickness.
·Edge non-straightness: The non-straightness of sheet edges should not exceed L 5 mm/n.
5 Barcol Hardness
For PMMA type solid surface materials: Grade A should be no less than 65, Grade B should be no less than 60.
For UPR type solid surface materials: Grade A should be no less than 60, Grade B should be no less than 55.
6.Load Deformation and Impact Toughness
For HI type solid surface materials, the maximum residual deflection value should not exceed 0.25 mm, and there should be no surface cracks after testing.
For Type II and Type IV sheets with a thickness less than 12.0 mm, this performance is not required.
Impact toughness of solid surface materials should be no less than 4.0 kJ/m2.
7 Falling Ball Impact
A 450g steel ball should impact at a height of not less than 2000 mm for Grade A and not less than 1200 mm for Grade B without damaging the sample.
8 Flexural Performance
The flexural strength of solid surface materials should be no less than 40 MPa, and the flexural modulus of elasticity should be no less than 6.5 GPa.
9 Wear Resistance
The wear resistance of solid surface materials should be tested according to the provisions of GB/T 17657-1999, using P120# emery cloth, 500g weight, and 500 revolutions. It should not exceed 0.6 g.
10 Coefficient of Expansion
The linear coefficient of expansion of solid surface materials should not exceed 5.0x10-5℃-1.
11 Color Fastness and Aging Performance
When compared to control samples, solid surface material samples should not exhibit any cracking, fissures, bubbles, or changes in surface texture. The color difference between the samples and control samples should not exceed 2 CIE units.
12 Radioactive Protection Classification Control
The radioactivity of artificial stone should comply with Class A requirements as specified in GB 6566.
13 Stain Resistance
The total stain resistance value for solid surface material samples should not exceed 64, and the maximum depth of stains should not exceed 0.12 mm.
14 Flame Resistance
Cigarette burning: Solid surface materials should not exhibit open flame combustion or smoldering during contact with a cigarette or afterward. Any form of damage should not affect product usability and can be approximately restored to the original state using abrasive and polishing agents.
Flame retardant performance: The flame retardant performance of solid surface materials should be evaluated by the oxygen index, and it should not be less than 40.
15 Chemical Resistance
Solid surface material test samples should show no significant damage when in contact with vinegar, detergent, citric acid (10% by mass), etc. Minor damage can be removed with 600-grit sandpaper, and the extent of damage should not affect the usability of the sheet and can be easily restored to the original state.
16 High-Temperature Performance
Solid surface material test samples should exhibit no significant effects such as cracking, fissures, or bubbling after 20 minutes of contact with a 180°C high-temperature object. Surface defects can be polished to restore them to the original state without affecting the usability of the sheet. During arbitration, the color difference between the repaired sample and the sample before testing should not exceed 2 CIE units.